Automation Anywhere is a powerful tool for automating business processes. One of its key features is Workload Management (WLM), which helps you manage and distribute tasks efficiently. Here’s a step-by-step guide to get you started with WLM Implementation in Automation Anywhere.
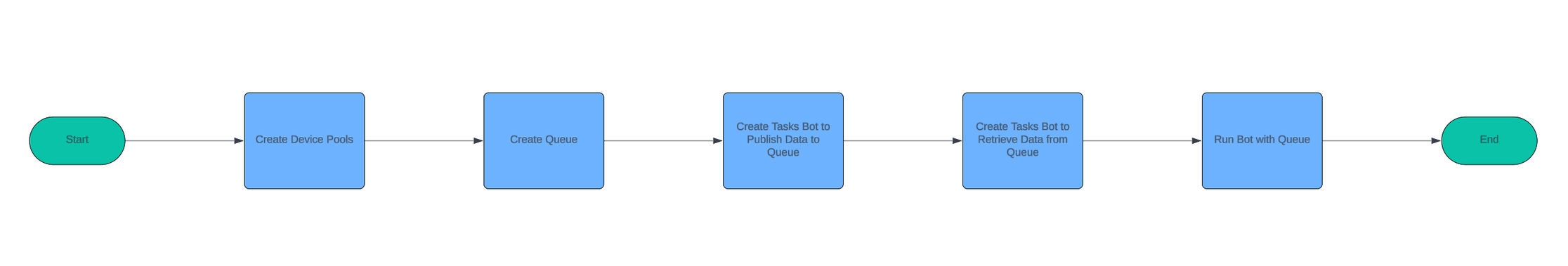
Step 1: Creating a Device Pool in Automation Anywhere A360
Creating a device pool in Automation Anywhere A360 helps you manage and allocate your bot runners efficiently.
- Log in to the Control Room: Use your credentials to log in to the Automation Anywhere A360 Control Room.
- Go to Device Pools: In the Control Room, click on the “Manage -> Device Pools” tab located in the left-hand menu.
- Create New Device Pool: Click on the “Create Device Pool” button in the top right.
- Enter Details: Provide a unique name and a brief description for your device pool.
- Select Devices: Add the required devices to the pool by selecting them from the list “Available Bot Runners” of available devices. Choose one or more device.
- Select Owners: Add the owners (Individual Users). Owner can View, Edit and delete the device pool.
- Select Consumer: Add the consumer (Roles: Group of users). Consumer can see the device pool as an option when they run a bot with Queue.
Step 2: Creating a Queue in Automation Anywhere A360
Creating a queue in Automation Anywhere A360 helps you manage and distribute tasks efficiently.
- Log in to the Control Room: Use your credentials to log in to the Automation Anywhere A360 Control Room.
- Go to Device Pools: In the Control Room, click on the “Manage -> Queues” tab located in the left-hand menu.
- Create New Queue: Click on the “Create Queue” button.
- Enter Details: Provide a unique name and a brief description for your queue.
- Set Parameters: Define the parameters such as priority, Reactivation Threshold, Max auto retry attempts and other relevant settings.
- Select Owners: Add the owners (Individual Users). Owner can Edit the queue and add new work items.
- Select Participants (Optional): Add the Participants (Roles: Group of users). Queue participants can add new work items and view the queue but cannot edit any other properties of the queue.
- Select Consumer (Optional): Add the consumer (Roles: Group of users). Queue consumer can view this queue and all the work items in the queue. In addition, they can use this queue when running bots.
- Define Work Item Structure: Use an Excel/CSV or Use Work item template (Existing work item template) or Manually (Create new work item template).
- Enter Work Item Structure: Enter work item template name, Add the required columns and sort the columns if needed.
- Add Work Items (Optional): Load the work items using Excel/CSV. The header of the excel file should be matched with the columns name. Duplicate records can be deleted by selecting the check box (Disallow duplicates).
Step 3: Creating Task Bots to Publish/Load data to Queue in Automation Anywhere A360
Creating tasks to Publish/Load data to a queue in Automation Anywhere A360 involves using the Bot Creator to define and map data fields.
- Log in to the Control Room: Use your credentials to log in to the Automation Anywhere A360 Control Room.
- Go to Automation: In the Control Room, click on the “Automation” tab located in the left-hand menu.
- Create Task Bot: Click on “Create a New Task” to start a new task (Queue Loader Task Bot).
- Add Command: In the task editor, search for the “Insert Work Item” command. Drag and drop the “Insert Work Item” command into the task editor.
- Select Queue: Choose the queue where you want to publish the data.
- Define Data Fields: Map the data fields from your source (e.g., Excel, CSV) to the queue fields.
- Map Fields: Ensure that each data field from your source is correctly mapped to the corresponding field in the queue.
- Add Data: Enter sample data to test the mapping.
- Save Task Bot: Save your task after configuring the “Insert Work Item” command.
- Test Task Bot: Run the task to ensure that data is being published to the queue correctly. Save and Test
- Deploy Task (Private to Public): Once tested, deploy the task to the Control Room for scheduling and execution.
Step 4: Creating Task Bots to Retrieve Data from a Queue in Automation Anywhere A360
Retrieving data from a queue in Automation Anywhere A360 involves using the Bot Creator to define and map data fields.
- Log in to the Control Room: Use your credentials to log in to the Automation Anywhere A360 Control Room.
- Go to Automation: In the Control Room, click on the “Automation” tab located in the left-hand menu.
- Create Task Bot: Click on “Create a New Task” to start a new task (Process Main Task Bot).
- Select Work Item Template: Go to work item template next to Close button. Select the Work item template.
- Retrieve Work Item: Use Work Item variable to retrieve the work item values using work item column name.
- Use Work Item Value: Work item value will be available in the “Process Main Task Bot”, you can use with in your process workflow.
- Save Task Bot: Save your task after configuring the “Work Item” with in your (Process Main Task Bot).
- Deploy Task (Private to Public): Once tested, deploy the task to the Control Room for scheduling and execution.
Step 5: Running a Bot with a Queue in Automation Anywhere A360
Running a bot with a queue in Automation Anywhere A360 allows you to efficiently process tasks by distributing them across multiple bot runners.
- Log in to the Control Room: Use your credentials to log in to the Automation Anywhere A360 Control Room.
- Go to Device Pools: In the Control Room, click on the “Manage -> Queues” tab located in the left-hand menu.
- Select Run Bot with Queue: Click on the “Run Bot with Queue” tab located in the Right-hand menu.
- Select Main Bot and Dependency: Select the main task with dependency.
- Select Queue: Choose the queue where you want to run the bot.
- Select Processing Time (Optional): Select the processing time if needed.
- Select Run As (Bot Runners): Select the bot runners where you want to run the bot. The bot runners should be part of the Device pool which will be used for this queue.
- Select Device Pool: Select the device pool that you have consumer access.
- Select Run Bot with Queue: Select run bot with Queue to Activate the queue.
- Pause Resume Stop: You can Pause, Resume and Stop the queue if needed during the execution.
Now, let’s dive deeper into the essential components and roles that make Workload Management (WLM) truly effective.
- Bot Creator: This is where the magic happens. Design and develop your bots with precision to ensure they meet your automation needs. Role: Bot Creator. Access: Full access to create, edit, and manage bots and queues.
- Bot Runner(s): Scale your operations with multiple Bot Runners. These environments execute your bots, handling tasks efficiently and effectively. Role: Bot Runner. Access: Execute bots and access queues to retrieve and process work items.
- Device Pools: Group your Bot Runners into device pools to balance the workload. This ensures efficient processing and maximizes your automation potential. Role: AAE_Pool Admin. Access: Create and manage device pools, assign Bot Runners to specific queues.
- Queue Access: Both Bot Creators and Bot Runners need seamless access to queues. This ensures that work items are managed and distributed smoothly, maintaining a steady workflow. Role: AAE_Queue Admin Access: View and manage my queues, create queues, administer all queues, and view my in-progress activity permissions.
- Control Room: Your central hub for configuration and monitoring. The Control Room allows you to manage queues, monitor bot performance, and ensure optimal operation. Role: Control Room Administrator. Access: Full access to configure and monitor the entire WLM setup, including queues, bots, and device pools.
- Work Item Templates: Define the structure of your data with these templates. They guide your bots with input and output parameters, ensuring consistent and accurate processing. Role: AAE_Queue Admin. Access: Create and manage work item templates, define input and output parameters.
FAQs
Whether you’re a seasoned automation expert or just starting out, these insights will help you streamline your operations and achieve better results.
🔍 Highlights include:
- How to create and manage workload queues
- Setting priorities for different tasks and queues
- Handling exceptions and reprocessing failed work items
- Monitoring performance and ensuring SLA compliance
1. What is Workload Management (WLM) in Automation Anywhere?
Workload Management (WLM) is a feature in Automation Anywhere that allows organizations to manage and distribute workloads across multiple bots. It helps prioritize high-value tasks and ensures that Service Level Agreements (SLAs) are met.
2. How do I create workload queues?
A workload queue holds data known as Work Items for further processing. The system distributes these Work Items to individual unattended Bot Runners in a device pool for processing.
3. What types of files can be uploaded for workload management?
Users can upload Microsoft Excel and CSV files to the Control Room, which then feeds the records from these files into the bot deployments.
4. What are the benefits of using WLM?
- Efficiency: Automates the distribution of tasks to available bots.
- Scalability: Easily add or remove bots based on workload.
- Utilization of Bot Runners: Fully utilizing the bot runners.
- SLA Management: Ensures tasks are completed within the defined SLAs.
5. How do I monitor the performance of workload queues?
You can monitor the performance of workload queues through the Control Room dashboard. It provides real-time insights into the status of Work Items, bot utilization, and SLA compliance.
7. Can I set priorities for different tasks in WLM?
Yes, you can set priorities for different tasks in Device pool. High-priority tasks can be processed first to ensure critical operations are completed on time.
8. How do I handle exceptions in Work Items?
Exceptions in Work Items can be managed by configuring exception handling in your bots. This includes retry mechanisms, logging errors, and notifying administrators.
9. What is the role of Bot Runners in WLM?
Bot Runners are responsible for executing the tasks assigned to them from the workload queues. They work in parallel to ensure efficient processing of tasks.
10. How can I scale my WLM setup?
You can scale your WLM setup by adding more Bot Runners to your device pool. This allows you to handle increased workloads without compromising on performance.
11. Is it possible to integrate WLM with other systems?
Yes, WLM can be integrated with other systems using APIs. This allows for seamless data exchange and better coordination between different platforms.
12. How do I ensure data security in WLM?
Data security in WLM can be ensured by implementing role-based access controls, encrypting data, and following best practices for data protection.
13. Can I use the same device pool for multiple queues in WLM?
Yes, you can use the same device pool for multiple queues in Workload Management (WLM) within Automation Anywhere. This allows you to efficiently manage and distribute tasks across different queues using the same set of Bot Runners, optimizing resource utilization and ensuring effective workload handling.
14. What happens if I have three queues using the same device pool? Which task will execute first?
When you have three queues using the same device pool, the execution order of tasks depends on the priority settings and the configuration of your queues:
- Priority Settings: Tasks from higher-priority queues will be executed first.
- Round-Robin Distribution: If no specific priorities are set, the system may use a round-robin or first-come, first-served approach.
15. How do I reprocess failed work items in the queue using a bot?
To reprocess failed work items using a bot:
- Create a Bot for Reprocessing: Design a bot that can handle the reprocessing of failed work items.
- Access the Queue: Use the Control Room API or interface to access the queue containing the failed work items.
- Retrieve Failed Work Items: Use the Get Queue Items command to retrieve failed work items.
- Process Each Failed Item: Loop through each failed work item, correct the issue, and update the status to “Re-process.”
- Update Work Item Status: Use the Update Queue Item command to change the status of the work item to “Re-process.”
- Log Results: Log the results of the reprocessing attempt, including any items that require manual intervention.





